News & Articles
Get up to speed on all the latest industry news, from ISO revisions to the latest research, and discover the newest products from Citation ISO Certification. You can also brush up on your business and ISO management skills using our detailed guides, crafted using insider knowledge from our experts.
ISO 9001 for Construction
In the construction industry, quality, safety, and efficiency are critical. Clients expect projects to be delivered on time, within budget, […]
How many clauses are there in ISO 9001:2015?
ISO 9001:2015 is the globally recognised Standard for Quality Management Systems, designed for organisations of all sizes and sectors to […]
How often is ISO 9001 updated?
When it comes to maintaining high standards in quality management, keeping up with updates to ISO 9001 is essential for […]
8 ways to maintain ISO 9001 certification
Maintaining your ISO 9001 certification might seem like a daunting task, but with the right approach, it can become an […]
How to conduct an ISO 9001 internal audit
An ISO 9001 internal audit is a critical component of maintaining an effective quality management system (QMS). It makes sure […]
How long does ISO 9001 certification last?
There’s a lot to compete with as a business so maintaining quality and excellence is more important than ever. One […]
What is the ISO 27001 Climate Change Amendment?
In February 2024, the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) introduced the Climate Action Changes amendment to the most widely used ISO Standards including 27001, 14001, 45001, and 9001.
ISO 9001 for Care
In the healthcare sector, maintaining high standards isn’t just essential for patient safety and satisfaction but for regulatory compliance too. […]
ISO 9001 for Manufacturing & The Importance
ISO 9001 for Manufacturing In the world of manufacturing, quality is everything. It’s what keeps customers happy and products safe. […]
Does ISO 9001 require a quality manual?
If you’re getting to grips with the ISO 9001 Standard, you might be wondering about a fundamental question: does ISO […]
6 ways ISO 9001 improves quality
Maintaining high–quality standards is crucial for overall success, and businesses should prioritise and demonstrate continuous improvement of the services they […]
Does ISO 9001 cover Health & Safety? Exploring the connection
ISO 9001 is a big name in quality management systems, but does ISO 9001 cover Health & Safety? Let’s take […]
What is a management review for ISO 9001?
A management review for ISO 9001 is a critical process that makes sure your organisation’s quality management system (QMS) remains […]
ISO 9001 for Service Companies
ISO 9001 might often be more associated with product based businesses, however its core principles and benefits are just as […]
What is the ISO 9001 Climate Change Amendment?
In February 2024, the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) introduced an ISO 9001 climate change amendment called the Climate Action […]
ISO 9001:2015 explained
ISO 9001 is a Standard that’s globally recognised for Quality Management Systems (QMS). Yes, the core principles remain the same, […]
ISO 27001 for the financial industry
As a financial business, your business relies on trust. Your customers trust banks, investment firms, and other financial institutions to […]
Using ISO 45001 and 45003 to manage psychosocial hazards
Today’s dynamic work environment demands that employers ensure the wellbeing of employees beyond physical safety. Psychological and social factors can […]
The similarities and differences between ISO 9001, ISO 14001 & ISO 45001
In the world of business, ISO certifications are what companies strive to achieve to ensure the quality, safety, efficiency, and […]
What is a corrective action?
In the world of quality management, it’s essential for businesses to not only maintain compliance but also adopt a proactive […]
The benefits of combining ISO 9001 and ISO 27001
An Integrated Management System (IMS) can benefit your organisation magnificently. If you’re looking to get ISO 9001 and ISO 27001 […]
What is the role of a certification body?
The exact role of a certification body can sometimes be a bit difficult to unpick, but we’re here to demystify […]
What is the difference between ISO 9001 and ISO 14001
In quality and environmental management, ISO Standards play a pivotal role in making sure organisations adhere to internationally accepted benchmarks. […]
Information Security vs Cyber Security: Recognising the difference
The difference between cyber security and information security might be small, but understanding the differences is a top priority if […]
ISO 27001 v 27002: What’s the difference?
Cyber security is important to all businesses but especially those scaling up. Businesses that don’t protect themselves as they grow can have a difficult time recovering from a cyber attack. Prioritising cyber security during business growth is essential to protect your business from threats that could hamper growth and the future of your business.
How physical security controls help businesses protect information
Physical security controls offer businesses protection against damaging attacks that threaten your information security. Keeping your data and information safe […]
How to write an ISO 27001 internal audit report
So, you’ve managed to attain certification to ISO 27001. You’ve strengthened your business’ information security, providing the platform for success. […]
How Information Security Risk Management protects against cyber threats
The constant evolution of cyber threats means businesses need to consider adopting information security risk management. As new technologies are […]
How to conduct an ISO 27001 gap analysis
Carrying out an ISO 27001 gap analysis might seem like a daunting task for your business. With multiple requirements, controls […]
The importance of an effective information security policy
Information security policies form the foundation of an organisation’s security and are featured as part of ISO 27001’s controls. But what are they and what should they include?
How ISO 27001 can help your business achieve cyber resilience
Cyber resilience is a business’ ability to prepare for, respond to, and recover from cyber threats and attacks while continuing […]
5 benefits of business continuity management systems
So, let’s paint a scenario, however far-fetched it may seem…your business is continuing to grow, going from strength to strength. […]
A Guide to ISO 14001
Implementing the ISO 27001 Management System does not necessarily mean that you have fulfilled your responsibilities as a business handling personal data in accordance with the GDPR, but it does mean you're well on your way.
Getting your ISO 27001 risk assessment right – our top tips
Identifying and responding to risks that threaten to compromise your information security should be an integral part of your responsibility […]
A Guide to ISO 27001
Implementing the ISO 27001 Management System does not necessarily mean that you have fulfilled your responsibilities as a business handling personal data in accordance with the GDPR, but it does mean you're well on your way.
Does ISO 27001 cover GDPR?
Implementing the ISO 27001 Management System does not necessarily mean that you have fulfilled your responsibilities as a business handling personal data in accordance with the GDPR, but it does mean you're well on your way.
A Guide to ISO 9001 in the workplace
Implementing the ISO 27001 Management System does not necessarily mean that you have fulfilled your responsibilities as a business handling personal data in accordance with the GDPR, but it does mean you're well on your way.
The difference between ISO 27001 and cyber essentials
Colleges and other education establishments are now required to implement ISO 27001 as part of their 2019/2020 contracts
ISO 27001 for education
Colleges and other education establishments are now required to implement ISO 27001 as part of their 2019/2020 contracts
10 common examples of ISO 14001 non-conformance
Does your organisation consider and manage its environmental impact? Everyday businesses are faced with increasing pressure from customers, regulators and governments to reduce their environmental impact.
ISO 27001 processes, policies and procedures
Colleges and other education establishments are now required to implement ISO 27001 as part of their 2019/2020 contracts
How does ISO 27001 help protect your organisation?
ISO 27001 is the international Standard for information security but how does it work to protect your organisation and its information?
What is the latest version of ISO 14001?
The ISO 14001 standard has been updated, but how will these changes affect businesses? ISO 14001:2015 follows the new Annex SL framework. It also includes more leadership responsibilities and addresses the environmental impact at all stages within product life cycle.
ISO 27001 for the Construction Industry
Cyber security is just as important in the construction industry as any other. With so much sensitive information stored within […]
ISO 27001 For The Retail Industry
Cyber security is all about how organisations work to reduce the risk of cyber attacks. They’re becoming ever more common […]
ISO 9001 processes, procedures and work Instructions
ISO 9001 processes and procedures are integral for meeting the requirements of the ISO 9001 management Standard. While businesses might […]
Why should you buy ISO 14001?
If you are looking to reduce waste management costs and demonstrate your business’ commitment to protecting the environment, implementing an environmental management system such as ISO 14001 can be a fitting solution.
A Guide to ISO Non-conformance
ISO non-conformance is the failure to meet one or more of the requirements outlined in management standard criteria. Whether it’s […]
How to Take Corrective Action Against ISO Non-conformance
What is ISO corrective action? In every business mistakes will happen, but it’s how you learn from these mistakes that […]
Cost of ISO non-conformance
ISO Standards are thought of as the global best practices by many industry leaders, so being ISO-certified shows your clients and customers that you’re a company to be trusted. But what happens when your business isn’t operating up to Standard? It’s known as non-conformance.
Managing sensitive online customer data? Here’s how to do it safely
By implementing some of the information security controls required by ISO 27001, you will be able to show due diligence to laws and regulations relating to data protection, like the GDPR and DPA.
How to make your business more energy efficient
With rising energy costs a challenge for every business you’ll want to make sure you’re being as efficient as possible and reducing your energy waste. Improving how you manage your energy can make a real difference to your business and the environment. So, it’s time for some positive energy, you’ve got the power to make changes to increase your energy efficiency, reduce your environmental impact, increase savings and boost your brand reputation.
A brand-new chapter
We’ve changed our name from QMS International to Citation ISO Certification. We’re the same great people providing the same great service, but our new and exciting rebrand is a truer reflection of who we are and we’re ready to share it with you.
ISOMentor – new courses now available
We’re excited to share that we now offer ISO 14001 and ISO 45001 (as well as ISO 9001) on our popular virtual training workshop service, ISOMentor.
Are you getting workplace wellbeing right?
The first Monday in February (which this year was 6 February) has been dubbed ‘National Sickie Day’. Statistically, it’s the day that more workers in the UK will call in sick than any other day.
Which ISOs are suitable for the construction industry?
Working in the construction industry, you probably have a good understanding of how competitive the market is. In order to successfully bid on projects, your construction firm must keep up to speed with industry demands. And this isn’t always easy without the right guidance… That’s where ISO Standards come into play!
Unpicking the ISO 27001:2022 changes
The much-anticipated 2022 update to the ISO 27001 Standard is here! Its official name – ISO/IEC 27001:2022 Information Security, Cybersecurity […]
5 ways to retain and engage your employees
Is employee disengagement or ‘quiet quitting’ if you want to be trendy, affecting your business? Odds are, it is. According […]
Why Health and Safety professionals need ISO 45001
We’ve all heard the saying safety first. So, when you’re responsible for the Health & Safety of employees and customers, […]
Which ISOs are suitable for smaller businesses?
At first glance, International Standards can seem tricky, time-consuming, and reserved for larger organisations but take a closer look and […]
The importance of compliance in manufacturing
When you work in manufacturing, you know compliance is key to meeting the standards expected of your business. From health and safety hazards to unsatisfactory goods, a breach in the system could damage operations. Such problems can lead to unhappy customers and harm the reputation of your business.
How to minimise the risk of workplace injury in the construction sector
According to the HSE, construction is ranked as one of the most dangerous industries to work in. In fact, the rate of fatal injury in construction is around four times as high as the average rate across all industries.
What is a purchasing procedure?
A purchasing procedure outlines the process of obtaining goods and services through your supply chain. As a business, you need […]
How can you cut musculoskeletal issues in the workplace?
Often, when we think of injuries in the workplace our minds jump to immediate accidents that happen without warning as a result of an incident like a trip, fire, or fall. However, one of the most common workplace injuries is musculoskeletal disorders.
Is your business losing recruits due to bad ESG credentials?
Research by business services provider DWF suggests that organisations who are failing to improve their environmental, social and governance (ESG) credentials are struggling to attract new talent.
Understanding the needs and expectations of interested parties for ISO 9001
To fulfil the requirements of clause 4 of your ISO, you must understand the needs and expectations of your interested parties. But who are your interested parties, and how do you manage their expectations
How can ISOs help businesses to reach COP26 goals?
The COP26 gathering in Glasgow brought home the importance of change to the way we run our businesses and live our lives. But what part can ISOs play in this?
What are the barriers to business’ environmental ambitions?
Customers, governments and campaigners all want businesses to embrace sustainability, but change is taking a long time to come. So, what’s stopping them?
What are the issues with carbon off-setting?
Carbon off-setting is being increasingly used by businesses to boost their green credentials. But how does it work and is it actually a useful tool for greater sustainability?
Meet ACS Requirements with ISO 9001/BS 10800
Create a tailored quality management system that also follows the recommendations of the new BS 10800 to help your security business meet the criteria of the Approved Contractor Scheme of the Security Industry Authority.
How do toolbox talks fit into ISO 45001?
Safety meetings such as toolbox talks are a great way to promote health & safety within an organisation. But what do they involve and how can they help you to meet ISO 45001 requirements?
The 101 on efficient warehouse management
Warehouse efficiency has long been relied upon for successfully servicing many industry sectors, but the recent boom of e-commerce has brought it even more into focus. A high level of organisation and quality communication is required to effectively manage a warehouse and consistently (and successfully) fulfil the end consumer’s needs. None of this is possible without efficient warehouse management.
How can ISO 9001 help sole traders?
ISO 9001 is an internationally recognised Standard for quality, but this doesn’t mean that it is only designed for large companies. Read on to find out how micro businesses and sole traders can also benefit from its processes.
All alone: what are the risks of lone working?
Lone working carries unique risks, and with approximately eight million people already working without others in the UK, employers need to know what they can do to keep them safe.
How can ISOs support mental well-being in the workplace?
Mental health in the workplace has become a priority issue, particularly after the effects of COVID-19. But how can ISOs help you to support your team’s mental well-being?
Case study: Efinity Labs
When the pandemic hit, Efinity Labs threw itself into sanitiser production. With a new product and new processes, the time was right to take quality to the next level with ISO 9001.
What are the 10 most common Occupational Health & Safety (OH&S) non-conformances found by ISO 45001?
If you're looking for advice on how to best apply the guiding principles of ISO 45001, our top 10 non-conformances could help you identify where improvements could be made.
What are the 10 most common non-conformances identified at an annual ISO 27001 surveillance audit?
Typical non-conformance can help you to identify where you could make improvements to your own processes and procedures to ensure you're getting the very best out of your ISO. Here is our ISO 27001 top 10.
What are the 10 most common environmental non-conformances identified by ISO 14001?
With the reduction of environmental impact an on-going hot topic, we've identified the top 10 non-conformances our customers identified through their ISO 14001 Certification.
Learning the risk: why risk assessments are key to your business
Risk assessments are key to keeping your workforce safe. But the changes brought by COVID-19 revealed that not all businesses are necessarily being proactive when it comes to assessing risk.
How do sole traders carry out a management review?
Management reviews are an essential part of ISO maintenance – but how do you carry them out if you are the only one in your business? Read on to find out.
What is a QMS?
Read on to find out what a QMS is, what it does and what benefits it can bring to any organisation, large or small.
Our Review Of The Back to Work Report
To find out how business adapted to the first national lockdown and how they recovered afterwards, we’ve created an in-depth report based on the results of our survey of SMEs.
Master the 8D method of problem-solving
A one-off non-conformity is common in any business, but if left to multiply, they can cause significant damage. Finding the root cause is key, and there are plenty of methods you can use. One of the most popular, particularly among larger companies, is the 8D method.
Testing, testing: how to test your business continuity plan
A robust business continuity plan can help your business get back on its feet after an unexpected interruption, such as an IT failure, powercut or pandemic. But a plan is only effective if it is implemented correctly, and the best way to determine that is to test it.
Everything you need to know about non-conformance in ISO 9001
Hunting for the root cause of a non-conformity and putting corrective action in place is all part and parcel of maintaining an ISO management system. But how do you go about it? To find out, check out our step-by-step guide.
What are the 5 key components of a business continuity plan?
The power goes off, you’re hit with a cyber-attack, a pandemic breaks out… disruption to your business can happen at any time, but how you react to it can make all the difference. A business continuity plan can ensure your reaction is the right one, but what does it involve?
Major vs Minor: Non-Conformance ISO
Non-conformances will often get flagged up in audits, but what is the difference between a major and a minor non-conformance? To dispel some of the confusion, we’ve put together a handy guide.
How can ISOs make your business disaster-proof?
Fire, flood, theft, a global pandemic… disaster can strike at any time. But with the right preparation and tools at your disposal, you can help your business to come out on top. Here’s how ISOs can help.
Risky business: why an out-of-date management system is a risk
Don’t let your standards slip with an out of date management system – upgrading is easier than you think.
What do I do if I’ve failed my ISO audit?
A detailed guide on what to do if you have failed an ISO audit and how you can recover from a failure.
How do you manage your management review?
Make your next management review one to remember with these top tips on how to keep them engaging.
Context of the Organisation Explained
An in-depth look at Clause 4 of the Annex SL structured ISO Standards, Context of the Organisation.
CDM Regulations explained
They’re the main regulations overseeing health, safety, and welfare across Britain’s construction industry, but how much do you know about CDM? Here, we take a closer look at these important legal duties
Are you ready to Tender?
An overview of the different types of tenders and the issues you should consider before responding
Management System maintenance: what do businesses need to do?
Ensuring that your Management System is kept up-to-date is one of the most important aspects of maintaining your certification to your chosen Standard. If you've ever wondered where to start; look no further.
Everything you need to know about ISO Management Systems
Are you struggling to get your head around ISO Management Systems? This comprehensive guide will tell you all the essentials and get you up to speed in no time!
A Beginner’s Guide to understanding SSIP Membership and Accreditation
What is SSIP? And what does it all mean? This blog explains SSIP membership and how businesses may become SSIP accredited. It also addresses the great benefits that SSIP accreditation can pose for buyers and suppliers. Finally, it provides insight into SMAS.
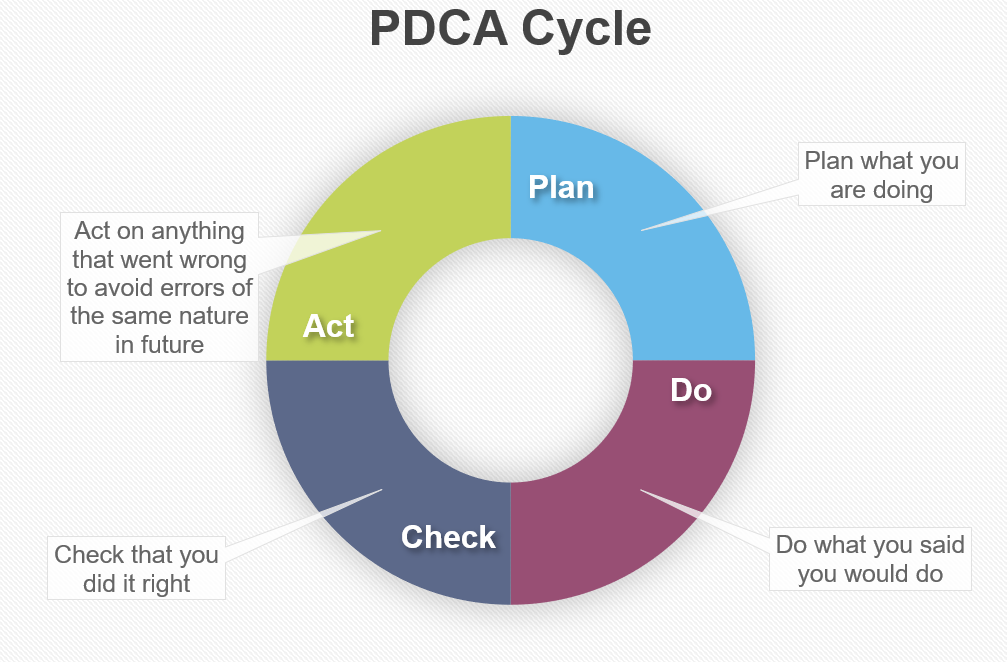
What is the Plan Do Check Act cycle?
Find out about the Plan Do Check Act cycle and how it works.
What is an Integrated Management System?
Find out about Integrated Management Systems and how they can help businesses like yours.
What is Annex SL?
Annex SL is the high-level structure for modern ISO Standards. The new structure ensures consistency and compatibility between the different Management System Standards.
Documented Management System vs ISO Manual
Documents that describe your Organisation's processes are referred to as a documented Management System. But how should you present these documents?
ISO 9001 vs other Quality Management Systems
Find out about the differences between an ISO 9001 certified Management System and other available Quality Management Systems.
How Will ISO 9001 Help Your Start-Up?
While often viewed as a tool for larger companies, ISO 9001 certification actually has equal power to boost the performance of start-up ventures. Here’s how:
The importance of engaging your team
Empowered and engaged employees bring many benefits to an organisation. Find out how you can get your employees on side and bring these benefits to your business.
The History of ISO 9001 Standards
In the year 2000, the ISO 9002 and ISO 9003 standards were retired and succeeded by a revised ISO 9001 - but is it a suitable replacement?
5 Tips to get the most out of an External Audit
External Audits ensure that your processes, systems and Manual are still appropriate and, more importantly, beneficial to your business. Find out how you can get the most out of yours with these five tips.
Tesco ordered to pay £125,000 for Health & Safety Breach
Tesco have been fined £116,000 and ordered to pay costs of more than £10,000 following an incident where an employee at their Highwoods store was injured.
Non-conformities – what are they and why do we need to check for them?
How to identify instances of non-conformity within a Management System and why it is important to do so.
5 tips to turn customer complaints into useful insight
People don’t like complaining – they do it because you have in some way annoyed or frustrated them. That is why it is important to remember these 5 important tips.
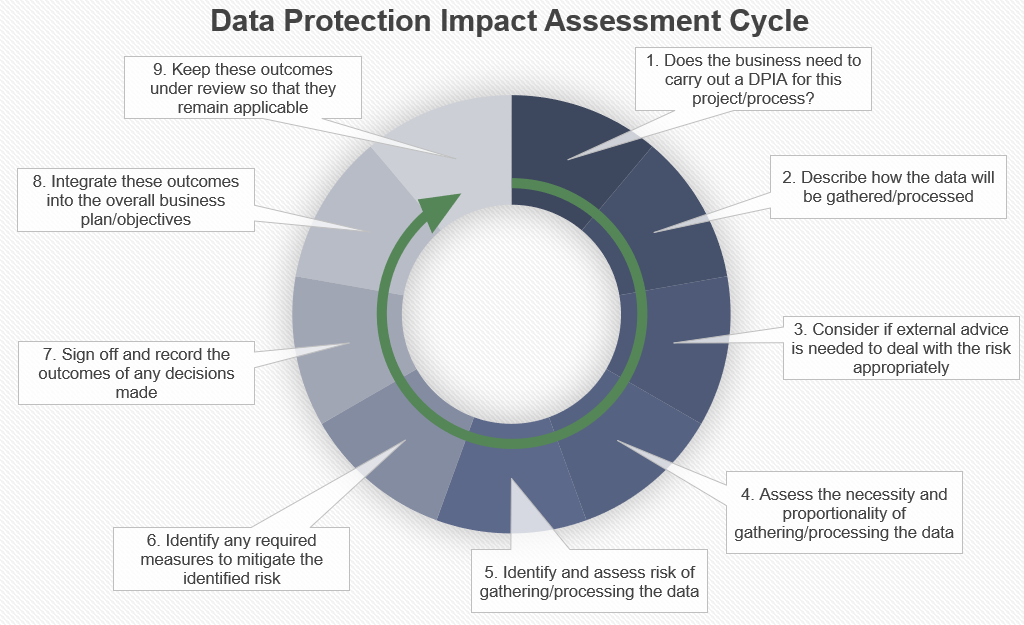
What is a Data Protection Impact Assessment?
Following recent updates to privacy legislation, businesses now need to build data protection into their products and processes right from the design stages.
ISO 14001 versus ISO 50001 – What are the Differences?
Businesses looking to become more environmentally responsible are turning to ISO 14001 certified Environmental Management Systems to help them with these aims. But there is a separate Standard, ISO 50001 Energy Management, which is causing confusion for businesses who are unsure
How does ISO 45001 add value to a conventional Health & Safety program?
Find out how businesses can improve their Health & Safety program by implementing an ISO 45001 Management System.
5 Tips to get the most out of a Management Review
A Management Review is a formal, structured meeting which involves top management and takes place at regular intervals throughout the year. They are a critical and required part of running an ISO certified Management System. Find out how you can run an effective Management Review
5 Tips to get the most out of a Supplier Audit
If you decide to carry out a Supplier Audit on the companies you work with, here are some practical tips to help you prepare, ensuring that you get the most out of the process.
5 Tips to get the most out of an Internal Audit
Internal Audits are scheduled periodic checks performed by businesses to ensure that their procedures are being followed as documented and are fit for purpose. Find out how they help your business to examine the operation and success of your Management System.
5 Ways to Improve the Consistency of your Organisation’s Operations
Discover how to maximise productivity and customer satisfaction by improving the consistency of your organisation’s operations
How to identify risks and keep trading following a service disruption
Find out what kind of risks can affect a business and what steps can you put in place to recover from these service disruptions - helping to maintain continuity in your service offering.
Information Security – Compliance and Certification
Information security isn’t a brand-new subject, but rapid advances in technology over recent years have made it much more challenging for organisations to protect personal data. Find out how you can protect your business.
How your management system can help to engage employees
A Management System is introduced to a business and requires regular input, from all areas, to be truly effective. Therefore, getting employees to engage with the Management System is vital. Find out how with these 10 tips.
Why Is ISO 9001 Important?
With so many different quality standards available, is ISO 9001 certification still important and valuable to businesses? And, perhaps more importantly, is it relevant to your industry in particular?